Griffonia simplicifolia is a remarkable plant native to West and Central Africa, widely recognized today for its natural production of 5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP). This climbing shrub has long been used in traditional medicine, yet its impact on modern neuroscience and supplementation has only recently been fully appreciated. The plant’s journey from African herbal traditions to global scientific research highlights its significance in both historical and modern health applications.
Discovery and Traditional Use in Africa
For centuries, the indigenous populations of Ghana, Côte d’Ivoire, and Togo have utilized Griffonia simplicifolia for its medicinal properties. Traditional healers prepared extracts from its seeds, leaves, and bark to address a variety of ailments, including wounds, infections, and digestive issues. However, one of its most well-documented uses was as a natural remedy for mood regulation and stress relief.
African healers would often crush the seeds or prepare decoctions to help individuals struggling with sadness, anxiety, or sleep disturbances. They may not have known the biochemical mechanisms at play, but they recognized the plant’s ability to influence emotional well-being and relaxation. Today, we understand that these effects stem from its high content of 5-HTP, a compound that directly contributes to serotonin production in the brain.
The Science Behind Griffonia Simplicifolia
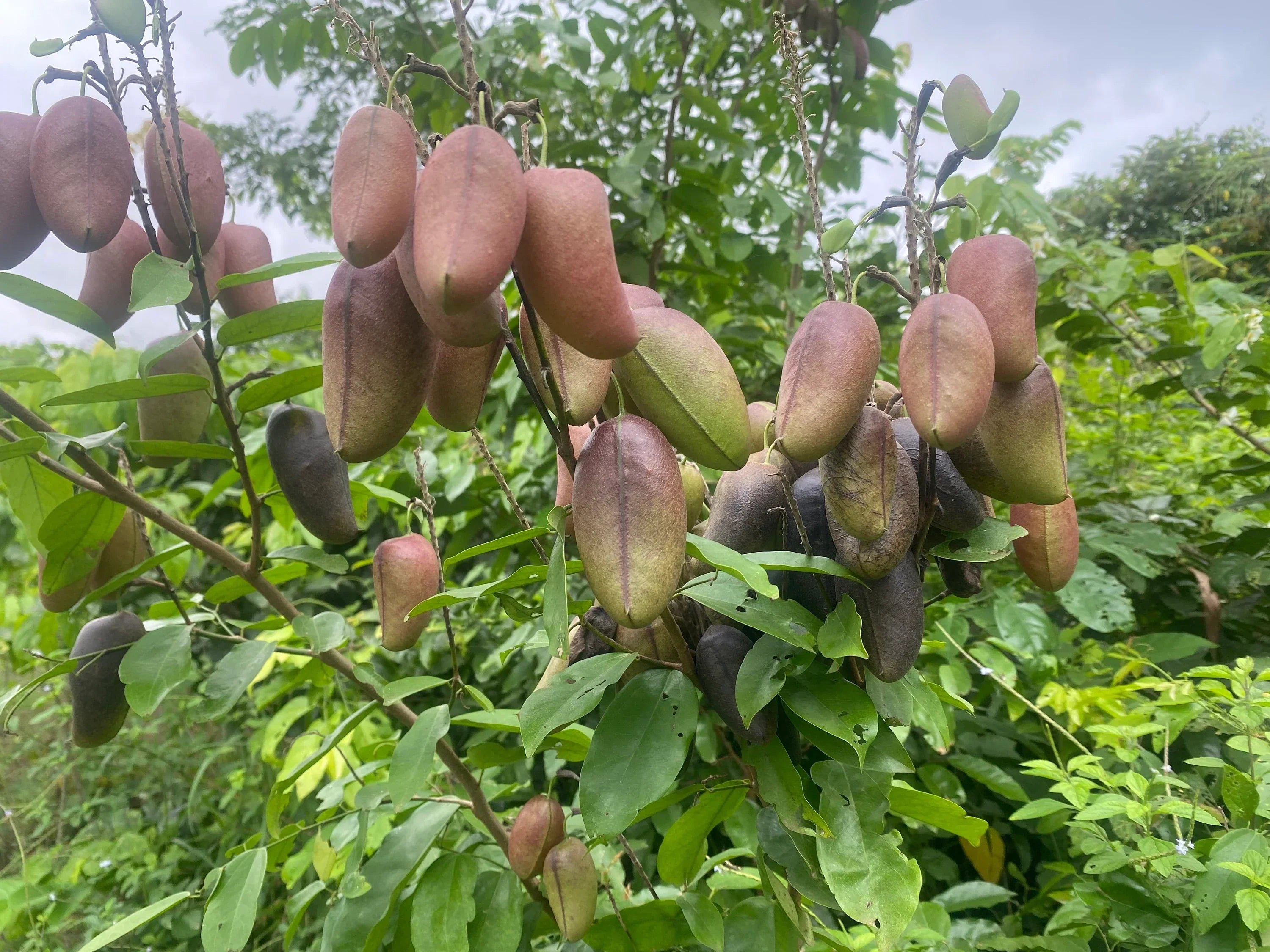
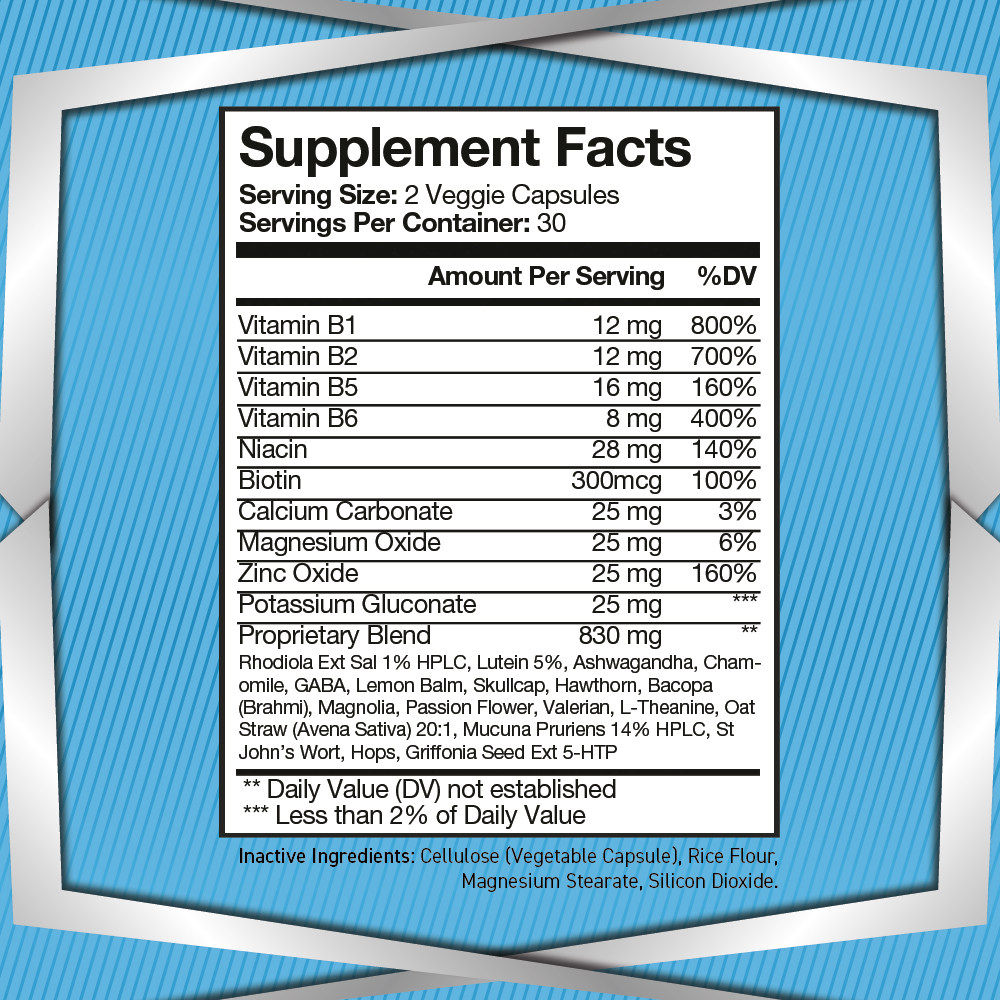
Griffonia simplicifolia produces large, black seeds that contain up to 20% 5-HTP by weight, making it one of the richest natural sources of this important compound. 5-HTP is an amino acid precursor to serotonin, a neurotransmitter responsible for regulating mood, appetite, and sleep. Unlike dietary sources of tryptophan, which must go through multiple biochemical steps before converting into serotonin, 5-HTP skips an important regulatory step, making it a more direct and efficient way to increase serotonin levels.
The discovery of Griffonia simplicifolia’s 5-HTP content sparked global interest in its potential applications. In the late 20th century, researchers began extracting 5-HTP from the plant for its therapeutic benefits, particularly in addressing conditions like depression, insomnia, and anxiety. This led to the development of 5-HTP supplements, which are now widely used to support brain health and emotional well-being.
Modern Applications and Supplementation
While Griffonia simplicifolia remains a natural source of 5-HTP, most commercial supplements today use synthesized 5-HTP to ensure purity, consistency, and sustainability. The plant-based extraction method requires harvesting large amounts of seeds, which can impact wild populations. Synthesizing 5-HTP in controlled environments helps meet demand while preserving natural ecosystems.
The benefits of 5-HTP supplementation derived from Griffonia simplicifolia have been extensively studied. Research indicates that it may:
-
Support mood balance: By increasing serotonin levels, 5-HTP helps regulate emotions and alleviate symptoms of stress and anxiety.
-
Promote better sleep: Since serotonin is a precursor to melatonin, 5-HTP indirectly enhances sleep quality.
-
Aid in appetite control: Serotonin influences satiety, making 5-HTP a valuable tool in managing cravings and weight regulation.
-
Enhance cognitive function: By optimizing serotonin levels, 5-HTP supports focus, memory, and overall mental clarity.
The Future of Griffonia Simplicifolia and 5-HTP Research
While 5-HTP supplements continue to be popular, research into Griffonia simplicifolia itself is ongoing. Scientists are exploring the plant’s other bioactive compounds, including potential antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, conservation efforts are being made to ensure sustainable harvesting practices, protecting the natural habitats where Griffonia simplicifolia thrives.
From its traditional roots in African medicine to its role in modern neuroscience, Griffonia simplicifolia remains one of nature’s most fascinating plants. Its contribution to serotonin research has revolutionized the way we approach mental health and well-being, bridging the gap between ancient wisdom and modern science.






































































1 comment
Samuel Donkor
Insightful. Thanks for the knowledge.