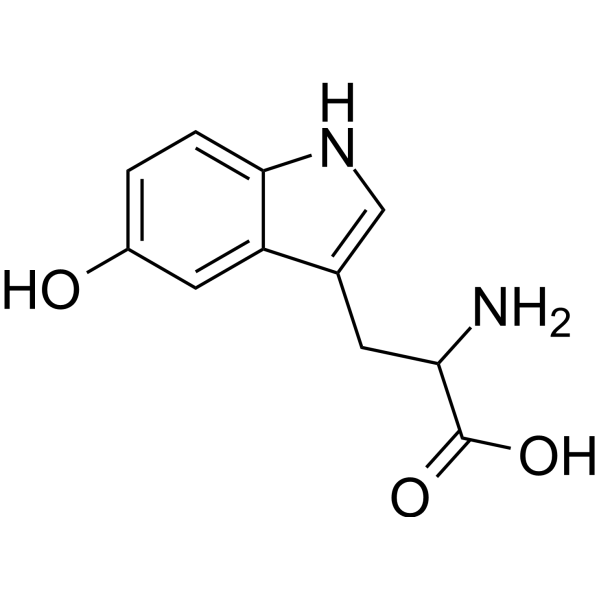
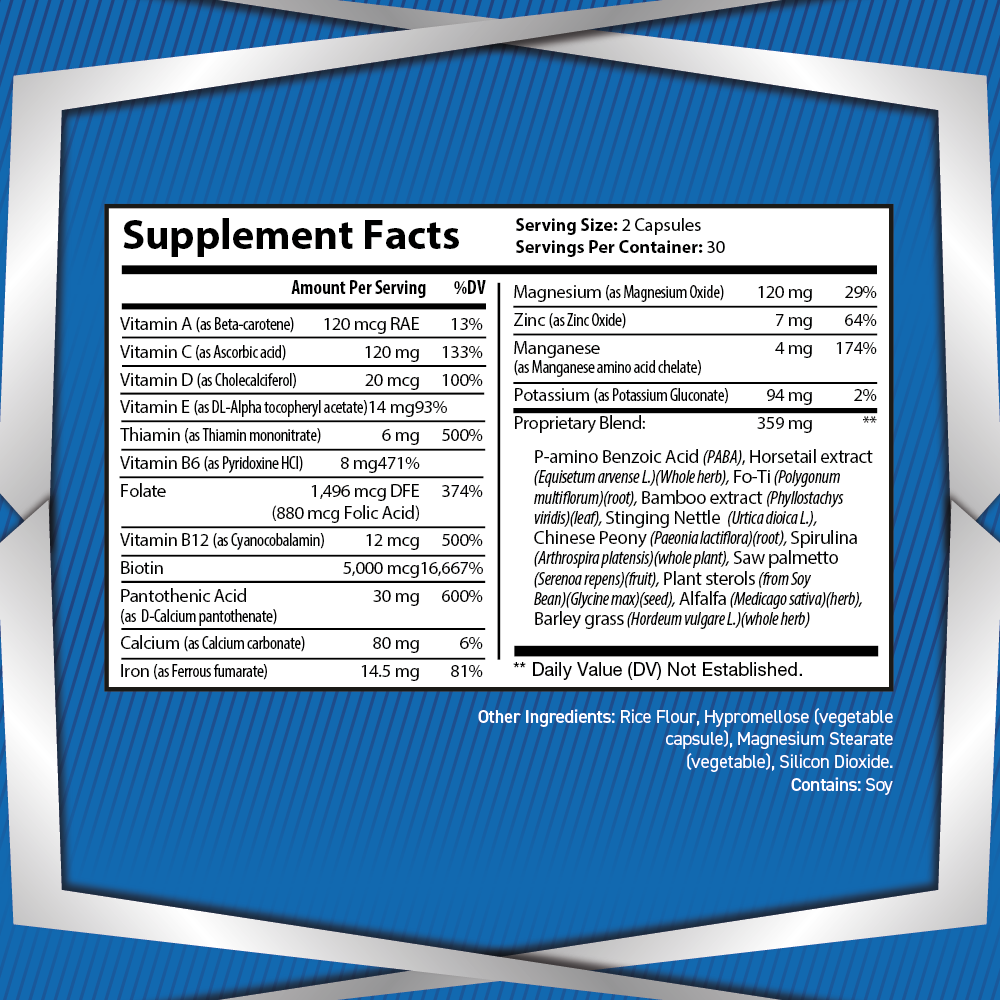
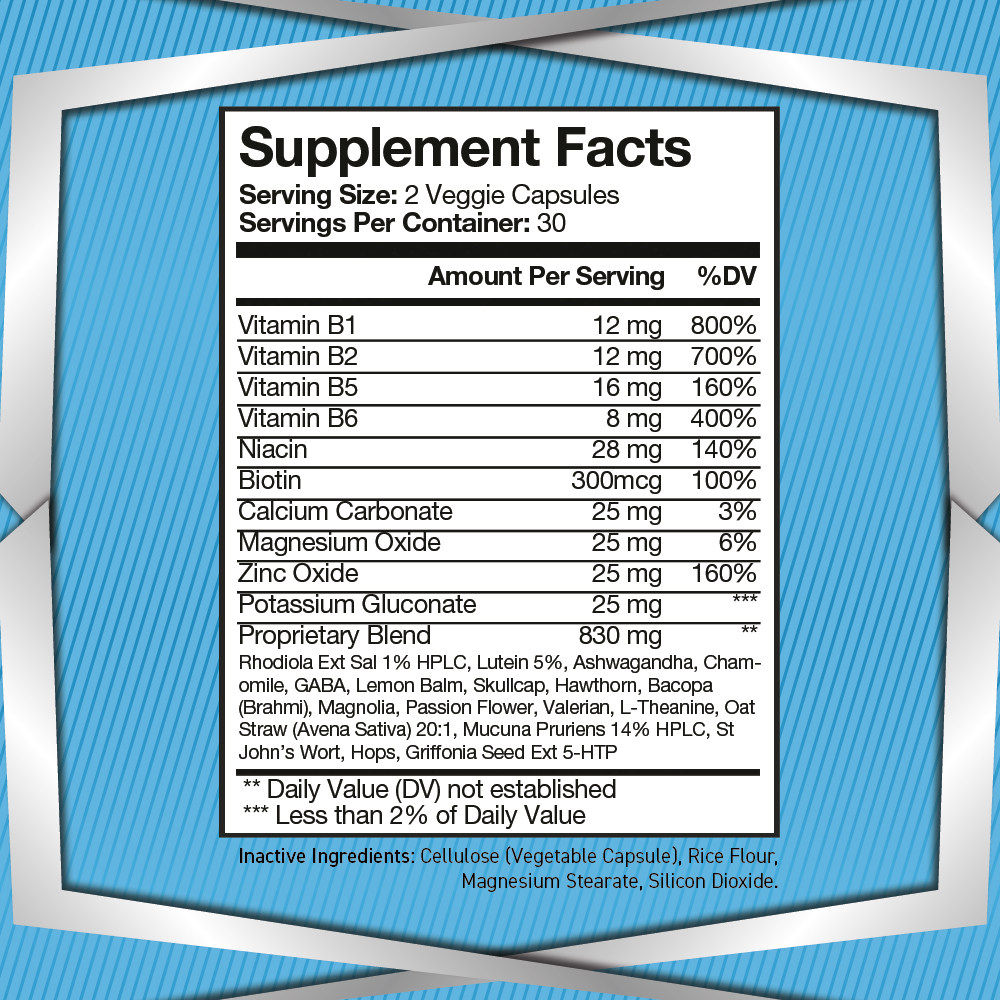
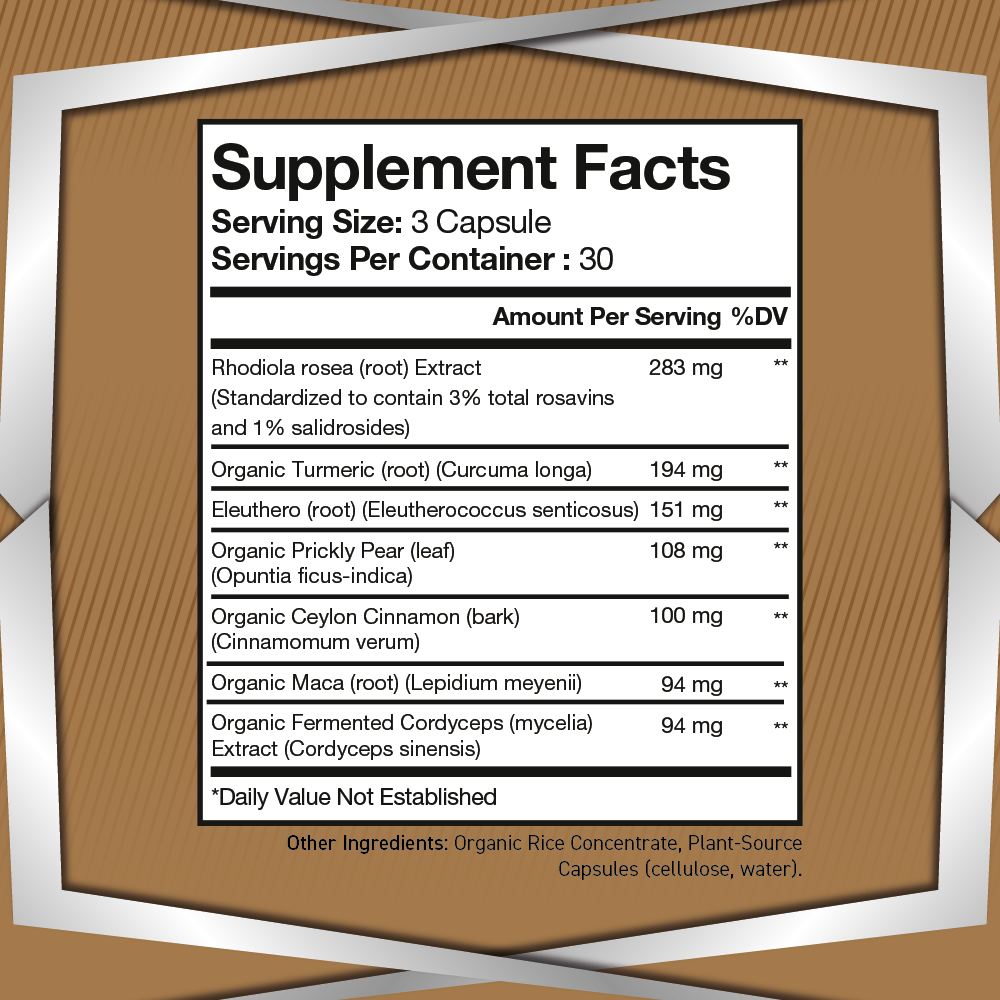
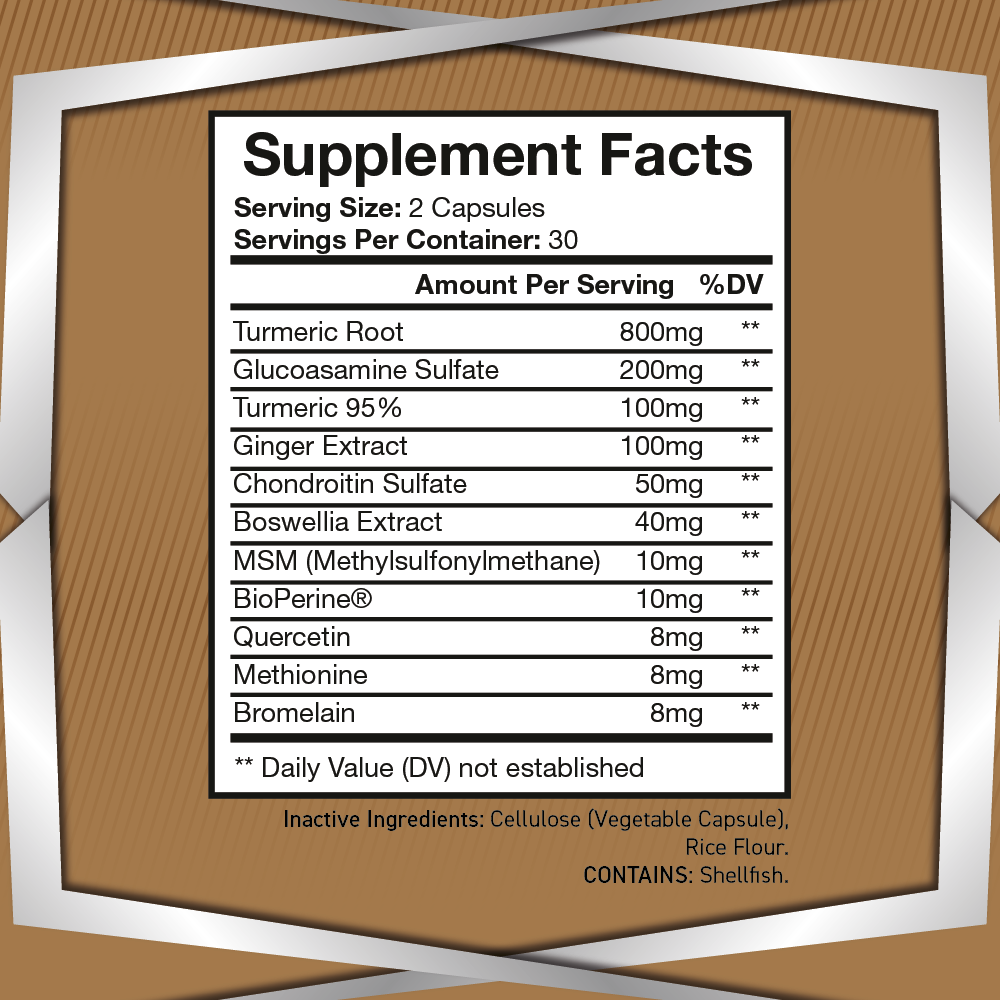
5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) is a naturally occurring amino acid and chemical precursor to serotonin, one of the brain’s most important neurotransmitters. As a critical component in the biosynthesis of serotonin, 5-HTP plays a vital role in regulating mood, sleep, and cognitive function. Its effects on the brain and body have made it a subject of great interest in neuroscience, psychology, and nutrition.
The Biochemical Pathway: From 5-HTP to Serotonin
5-HTP is derived from L-Tryptophan, an essential amino acid obtained through diet. Once inside the body, L-Tryptophan is converted into 5-HTP by the enzyme tryptophan hydroxylase. This reaction is a crucial step in serotonin production, as 5-HTP then undergoes decarboxylation by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AAAD), transforming into serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, or 5-HT). Unlike L-Tryptophan, 5-HTP readily crosses the blood-brain barrier, making it a more direct and efficient precursor to serotonin.
Serotonin, often referred to as the "happiness molecule," is involved in various physiological functions, including mood regulation, appetite control, sleep cycles, and cognitive flexibility. Deficiencies in serotonin have been linked to conditions such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders, making 5-HTP supplementation a promising tool in supporting mental well-being.
How 5-HTP Affects Brain Chemistry
What makes 5-HTP unique is its ability to bypass the rate-limiting step in serotonin synthesis. The conversion of L-Tryptophan into 5-HTP is highly regulated and affected by external factors such as stress, inflammation, and diet. However, when 5-HTP is introduced directly, it skips this regulation, allowing for a more consistent and efficient production of serotonin. This has made 5-HTP a popular subject of research in mood disorders, particularly for individuals with serotonin imbalances.
Additionally, serotonin is a precursor to melatonin, the hormone responsible for regulating sleep-wake cycles. By increasing serotonin availability, 5-HTP indirectly enhances melatonin production, supporting better sleep quality and overall circadian rhythm regulation.
Potential Benefits of 5-HTP Supplementation
Because of its role in serotonin synthesis, 5-HTP has been studied for its potential benefits in mental and physical health. Research suggests that 5-HTP supplementation may:
-
Support mood balance: By increasing serotonin levels, 5-HTP may help alleviate symptoms of low mood, stress, and irritability.
-
Improve sleep quality: Higher serotonin levels contribute to better melatonin production, promoting deeper and more restorative sleep.
-
Aid in appetite control: Serotonin plays a key role in regulating hunger, and 5-HTP has been linked to reduced cravings and improved satiety.
-
Support neurological function: Serotonin is critical for cognitive flexibility, learning, and overall mental clarity.
The Scientific Perspective
While 5-HTP is naturally occurring, its supplementation should be approached with care. Because it directly influences serotonin production, excessive use could lead to imbalances, particularly when combined with serotonin-targeting medications like SSRIs. This is why research continues to explore optimal dosages and mechanisms to ensure safe and effective use.
As an advanced neurochemical tool, 5-HTP provides fascinating insights into the interplay between neurotransmitters and mental well-being. Its ability to support serotonin production makes it a valuable component in modern approaches to mood, sleep, and cognitive health. With ongoing research, the full potential of 5-HTP continues to unfold, offering new pathways for optimizing brain chemistry and enhancing quality of life.